View pictures in App save up to 80% data.
Reiter Syndrome, often referred to as reactive arthritis, is an uncommon disorder characterized by inflammation in multiple areas of the body. Commonly impacted regions include the joints, eyes, and urinary system. Gaining insight into this condition can aid in symptom management and enhance overall quality of life.
- Reiter Syndrome is named after Hans Reiter, a German physician who first described the condition in 1916.
- It is often triggered by an infection, particularly in the intestines, genitals, or urinary tract.
- The condition is more common in men than women, especially those between the ages of 20 and 40.
- Symptoms usually appear within 1 to 4 weeks after the initial infection.
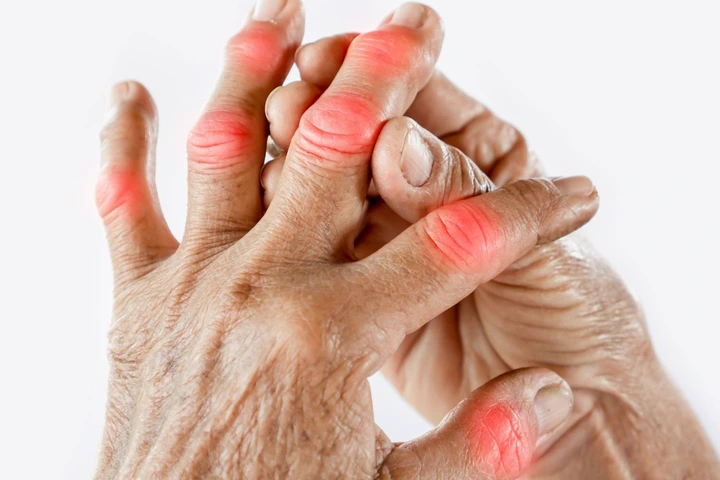
- Common symptoms include joint pain, redness, and swelling, particularly in the knees, ankles, and feet.
- Eye inflammation, known as conjunctivitis, is another hallmark symptom.
- Urethritis, or inflammation of the urinary tract, can cause pain during urination.
- Some people may develop skin rashes or sores, particularly on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
- The exact cause of Reiter Syndrome is unknown, but it is believed to involve an abnormal immune response.
- Genetic factors may play a role, as the condition is more common in people with the HLA-B27 gene.
Assessment and Management
Identifying Reiter Syndrome can be difficult because of its diverse symptoms. Nevertheless, prompt diagnosis and intervention are essential for effectively managing the condition.
- There is no single test for Reiter Syndrome; diagnosis is usually based on medical history and symptoms.
- Blood tests can help identify markers of inflammation and rule out other conditions.
- Joint fluid analysis may be performed to check for signs of infection or inflammation.
- Imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs can help assess joint damage.
- Treatment typically involves managing symptoms with medications and lifestyle changes.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Corticosteroids may be prescribed for severe inflammation.
- Antibiotics are used to treat the underlying infection that triggered the condition.
- Physical therapy can help maintain joint function and flexibility.
- Regular exercise is important for overall health and can help reduce symptoms.
Experiencing Life with Reiter's Syndrome
Experiencing Life with Reiter's Syndrome can be challenging, but with proper management, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Here are some tips and facts to help navigate daily life with this condition.
- Maintaining a healthy diet can help reduce inflammation and improve overall well-being.
- Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil, may have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Avoiding foods that trigger inflammation, such as processed foods and sugary drinks, is beneficial.
- Stress management techniques, like meditation and yoga, can help reduce symptoms.
- Getting enough sleep is crucial for managing pain and fatigue.
- Support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice.
- Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are important for monitoring the condition.
- Smoking can worsen symptoms, so quitting is highly recommended.
- Alcohol consumption should be limited, as it can interfere with medications and exacerbate symptoms.
- Wearing comfortable, supportive shoes can help reduce foot pain.
Complications and Expected Outcomes
Although numerous individuals with Reiter Syndrome achieve complete recovery, a portion may face ongoing complications. Being aware of these possible challenges can aid in better managing the condition.
- Chronic arthritis can develop in some individuals, leading to long-term joint pain and stiffness.
- Eye inflammation can recur, potentially causing vision problems if not treated promptly.
- Heart problems, such as inflammation of the heart muscle or valves, are rare but possible.
- Kidney issues, including inflammation and damage, can occur in severe cases.
- Skin problems, like psoriasis, may develop or worsen.
- Gastrointestinal issues, such as inflammatory bowel disease, can be associated with Reiter Syndrome.
- The condition can affect mental health, leading to anxiety or depression.
- Early and aggressive treatment can help prevent long-term complications.
- Regular monitoring and follow-up care are essential for managing the condition.
- With proper treatment, many people can achieve remission and lead active lives.
Investigation and Prospective Pathways
Continued research is essential for gaining a deeper insight into Reiter Syndrome and creating improved treatment options. Below are some of the latest discoveries and potential avenues for future exploration in this area.
- Researchers are studying the role of genetics in Reiter Syndrome to identify potential risk factors.
- New medications are being developed to target specific inflammatory pathways.
- Advances in imaging technology are improving the ability to diagnose and monitor the condition.
- Studies are exploring the impact of diet and lifestyle on symptom management.
- Researchers are investigating the potential benefits of alternative therapies, such as acupuncture and herbal medicine.
- Clinical trials are testing new treatments and therapies for Reiter Syndrome.
- Patient registries and databases are helping to collect valuable information on the condition.
- Collaboration between researchers, healthcare providers, and patients is essential for advancing knowledge and treatment.
- Increased awareness and education about Reiter Syndrome can lead to earlier diagnosis and better outcomes.
- Continued research and innovation hold promise for improving the lives of those affected by Reiter Syndrome.
Concluding Reflections on Reiter's Syndrome
Reiter Syndrome, also known as Reactive Arthritis, is a complex condition that can significantly impact daily life. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for managing the disease effectively. Early diagnosis and intervention can make a world of difference, helping to alleviate pain and improve mobility. Remember, while there's no cure, various treatments like medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms. If you or someone you know is experiencing signs of Reiter Syndrome, consult a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation. Staying informed and proactive is key to living a healthier, more comfortable life despite the challenges posed by this condition. Keep learning, stay vigilant, and don't hesitate to seek support when needed.
Commonly Asked Questions
Reiter Syndrome, also known as reactive arthritis, is a type of inflammatory arthritis that can occur as a reaction to an infection in another part of the body. It typically manifests with symptoms such as joint pain and swelling, often affecting the knees, ankles, and feet. Other common features include urethritis (inflammation of the urethra) and conjunctivitis (inflammation of the eyes). The condition is often associated with certain infections, particularly those caused by bacteria such as Chlamydia or gastrointestinal pathogens. Reiter Syndrome can vary in duration, with some individuals experiencing chronic symptoms while others may see resolution over time. Treatment generally focuses on relieving symptoms and may involve nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or other medications.
Reiter Syndrome, often referred to as reactive arthritis, occurs as a reaction to an infection occurring elsewhere in the body. This syndrome mainly affects the joints, eyes, and urinary system, resulting in various symptoms such as discomfort, inflammation, and discoloration.
Reiter Syndrome, also known as reactive arthritis, typically occurs as a reaction to an infection in another part of the body. It is often triggered by bacterial infections, particularly those affecting the urogenital or gastrointestinal systems, such as chlamydia or salmonella. The exact cause of why some individuals develop Reiter Syndrome while others do not is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic predisposition and immune response to infection. Symptoms can include joint pain, inflammation, and other systemic manifestations.
This syndrome frequently occurs after an infection, especially those affecting the gastrointestinal or genitourinary systems. Typical offenders include specific bacteria such as Chlamydia and Salmonella. Once your body has successfully dealt with the initial infection, the immune system may erroneously target healthy tissue, leading to the onset of symptoms associated with Reiter Syndrome.
Is there a cure for Reiter Syndrome?
Although there isn't a definitive cure for Reiter Syndrome, many individuals experience relief through various treatments. These may involve medications aimed at alleviating inflammation and discomfort, antibiotics to address any persistent infections, and physical therapy to maintain joint flexibility and strength. With appropriate care, symptoms can greatly improve or even become completely absent for certain durations.
Who is susceptible to developing Reiter Syndrome?
Reiter Syndrome can affect anyone, but it tends to be more prevalent among men aged 20 to 40. Genetic factors are significant as well; individuals carrying the HLA-B27 gene face a greater likelihood of developing the condition. Furthermore, a background of infections that may provoke the syndrome can elevate one's risk.
Reiter Syndrome, also known as reactive arthritis, typically presents with a combination of symptoms that may include: 1. Joint pain and swelling, often affecting the knees, ankles, and feet. 2. Inflammation of the eyes, leading to conditions such as conjunctivitis or uveitis. 3. Urinary tract symptoms, such as burning during urination or increased frequency. 4. Skin rashes, which can appear as lesions or sores. 5. Fatigue and general malaise. These symptoms can develop after an infection in the gastrointestinal or urogenital tract. It's important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Symptoms can differ from person to person, but they frequently involve joint discomfort and swelling, difficulties with urination, and inflammation of the eyes. Additionally, some individuals may face skin irritations or ulcers in the mouth. These symptoms may develop slowly over time or appear abruptly, varying in intensity from mild to severe.
Is Reiter's Syndrome contagious?
No, Reiter Syndrome is not contagious. The infections that may cause the syndrome can be transmitted, but the syndrome itself is a result of the body’s response to these infections, rather than the direct transmission of an infectious agent between individuals.
Reiter Syndrome, also known as reactive arthritis, can vary in duration from person to person. Some individuals may experience symptoms for a few weeks to several months, while others may have recurrent episodes over a longer period. In many cases, symptoms tend to improve within six months, but it's important to consult a healthcare professional for personalized information and management.
The length of time symptoms last can differ significantly. While some individuals might have symptoms that persist for a few weeks or months before they fade away, others may struggle with symptoms for extended durations, or they may experience fluctuations in their severity. Seeking assistance from healthcare providers can be beneficial in managing the condition, potentially leading to a decrease in both the duration and intensity of symptoms.
Can adjustments in lifestyle assist in managing Reiter Syndrome?
Certainly! In addition to medical interventions, adopting a healthier lifestyle can significantly impact your health. Engaging in regular physical activity, keeping a healthy weight, and consuming a nutritious diet can aid in symptom management and enhance overall wellness. Additionally, for some individuals, reducing stress levels and steering clear of activities that put pressure on affected joints can prove advantageous.
Did you find this page useful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.