View pictures in App save up to 80% data.
How intermittent fasting and protein timing enhance metabolic rate
Intermittent fasting and protein pacing have become a popular duo for improving metabolic health and weight management. By strategically timing protein intake with fasting windows, this approach taps into the body’s natural fat-burning mechanisms while preserving lean muscle mass. This synchronization between fasting and nutrition creates an optimal environment for the body to burn fat more effectively, helping to maintain a healthy weight over the long term.
Recent studies suggest that intermittent fasting activates key metabolic pathways that increase fat oxidation, or the breakdown of fat for energy. However, one of the common concerns with fasting is the potential loss of muscle mass, particularly during extended fasting periods. Protein pacing, where protein intake is spread out throughout the day in targeted intervals, helps to mitigate this issue by ensuring that the body has a steady supply of the building blocks it needs to preserve muscle. The synergy between these two approaches maximizes fat-burning potential while preventing muscle breakdown, making it a compelling strategy for those looking to manage their weight and improve their body composition.
Enhancing microbiome health
An essential factor to consider when integrating intermittent fasting with protein pacing is its effect on the gut microbiome. The human microbiome, which consists of a wide array of bacteria within our digestive tract, is crucial for managing metabolism, aiding digestion, and controlling inflammation. Studies indicate that both fasting and protein consumption affect the composition of the microbiome, and their combination can promote a more balanced and diverse population of gut bacteria, leading to improved overall gut health.
Fasting intervals give the digestive system a chance to rest, enabling the microbiome to reset. A more balanced microbiome can result in better metabolic performance, improved digestion, and lower levels of inflammation—all of which are essential for overall well-being. At the same time, incorporating protein from high-quality sources such as lean meats, legumes, and dairy provides vital nutrients that bolster gut health and immune response. The interplay between fasting and adequate protein intake appears to create favorable conditions for a healthy gut, which may subsequently enhance metabolism and facilitate effective weight control.
Hormonal balance
Understanding the interplay between intermittent fasting, protein timing, and hormonal control is crucial to grasping the effectiveness of this dietary method. Both the periods of fasting and the timing of protein intake have significant effects on various hormones that regulate hunger, fullness, and metabolic processes, including insulin, ghrelin, and leptin. By coordinating protein consumption with fasting intervals, these hormones collaborate to boost fat oxidation and enhance overall body composition.
For example, intermittent fasting can effectively reduce insulin levels, which in turn encourages the breakdown of fat and supports weight loss. At the same time, the strategic timing of protein intake during eating periods aids in managing hunger hormones such as ghrelin, which drives appetite, and leptin, which indicates fullness. This harmonious method of balancing hormones can diminish cravings, enhance feelings of fullness post-meal, and create a more conducive metabolic setting for managing weight. Ultimately, this forms a holistic approach to enhancing metabolic health and decreasing body fat without resorting to strict dieting.
Practical execution
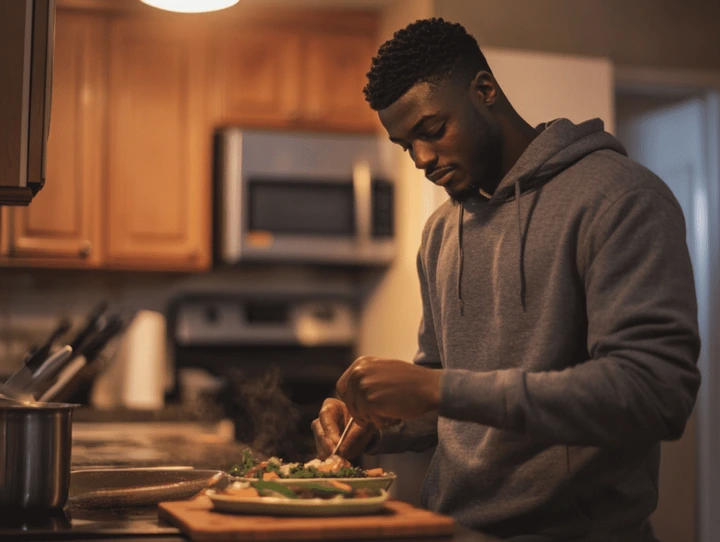
The science of merging intermittent fasting with protein pacing may seem intricate, but implementing this strategy can be quite simple with proper planning. For those just beginning with intermittent fasting, it's advisable to initiate with a reasonable fasting period, like 12 hours, and progressively extend it as the body gets accustomed. During the specified eating windows, meals high in protein should be consumed, distributed evenly throughout the day to enhance muscle protein synthesis and promote overall metabolic well-being.
A common strategy could include a fasting period of 16 hours, followed by an 8-hour window for eating. Within this eating window, individuals should aim to have 3 to 4 meals rich in protein, making sure to distribute their protein intake evenly throughout the day. The timing of these meals plays a significant role, as eating protein too near the beginning or end of the fasting period may diminish its benefits for muscle maintenance and metabolic well-being.
Sustainable practices for the long haul
The effectiveness of combining intermittent fasting with protein pacing stems from its potential to induce sustainable metabolic changes while being adaptable to different lifestyles. This method isn't universally applicable; individuals must tailor their fasting and eating periods to suit their specific requirements and routines. Paying attention to one's body is crucial, as it allows for adjustments in protein consumption and fasting lengths according to personal reactions and objectives.
A major benefit of this approach is its sustainability. In contrast to strict diets that are often hard to stick with in the long run, intermittent fasting combined with protein pacing offers a more flexible and balanced eating strategy. By staying aware of their protein consumption, fasting intervals, and overall dietary choices, individuals can enjoy the advantages of enhanced metabolism and effective weight management over time. Furthermore, as ongoing research sheds light on this method, new findings could enhance its effectiveness, making it an even more user-friendly option for maintaining a healthy weight and supporting metabolic well-being.